Inspection News
Barcode Types: A Comprehensive Guide for Businesses and Consumers – Part 1
Barcodes are ubiquitous in today’s world, gracing everything from grocery items to pharmaceutical packaging. These seemingly simple patterns of parallel lines hold a wealth of information, enabling efficient product identification, tracking, and inventory management. Understanding the different types of barcodes and their applications is crucial for businesses and consumers alike.
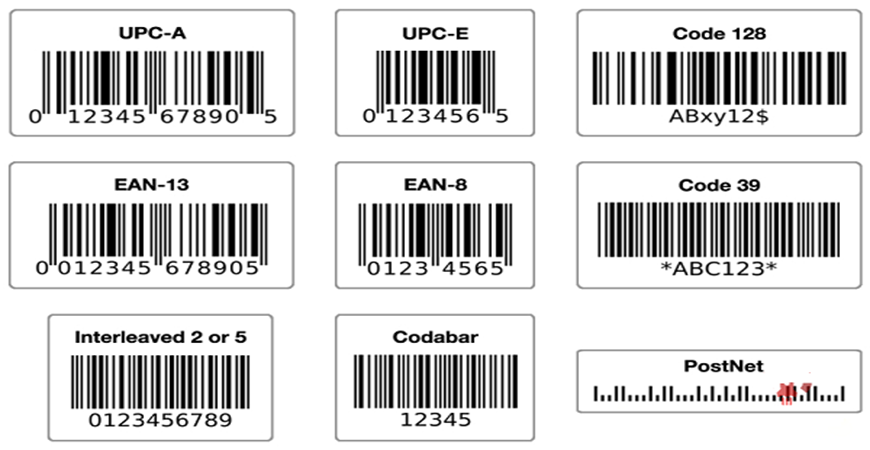
1. UPC (Universal Product Code) Barcodes
Predominantly used in the United States and Canada, UPC barcodes are the standard for encoding product information in retail settings. They come in two main variants:
-
UPC-A: Encodes 12 digits, commonly found on consumer goods in North America.
-
UPC-E: Encodes 6 digits, a shortened version for smaller products or those with limited label space.

2. EAN (European Article Number) Barcodes
Similar to UPC barcodes, EAN barcodes are widely used in Europe and other regions for product identification. They also have two primary variants:
-
EAN-13: Encodes 13 digits, the standard for most retail products in Europe.
-
EAN-8: Encodes 8 digits, used for smaller products or those with limited label space.
3. Code 39 Barcodes
Versatility is the hallmark of Code 39 barcodes, as they can encode all alphabetic characters, numerals, and some special symbols. Their accuracy and reliability make them ideal for applications like:
-
Inventory Management: Tracking and managing stock levels in warehouses and retail environments.
-
Asset Tracking: Monitoring and controlling the movement of valuable equipment and assets.
-
Inventory Control: Maintaining accurate records of product availability and preventing stockouts.
4. Code 128 Barcodes
Code 128 barcodes take data density to the next level, capable of encoding the entire ASCII character set, including extended characters. This high-capacity feature makes them suitable for applications requiring extensive information, such as:
-
Shipping and Logistics: Labeling packages and tracking their movement throughout the supply chain.
-
Manufacturing: Identifying components and parts in complex manufacturing processes.
-
Healthcare: Labeling medical devices and patient records for accurate identification.
Conclusion
Barcodes stand as a testament to technological advancement, providing numerous practical benefits to society and contributing to enhanced operational efficiency across various sectors. With the continuous evolution of science and technology, barcodes will undoubtedly continue to play a pivotal role in information management, process automation, and improving the quality of our lives.
If you need professional quality control inspection services, contact VIS today! We ensure your product quality every step of the way!